The material below comprises excerpts from books by Dr. Johnathan Mun, our CEO and founder, such as Readings in Certified Quantitative Risk Management, 3rd Edition, and Quantitative Research Methods Using Risk Simulator and ROV BizStats Software Applying Econometrics, Multivariate Regression, Parametric and Nonparametric Hypothesis Testing, Monte Carlo Risk Simulation, Predictive Modeling, and Optimization, 4th Edition (https://www.amazon.com/author/johnathanmun). All screenshots and analytical models are run using the ROV Risk Simulator and ROV BizStats software applications. Statistical results shown are computed using Risk Simulator or BizStats. Online Training Videos are also available on these topics as well as the Certified in Quantitative Risk Management (CQRM) certification program. All materials are copyrighted as well as patent protected under international law, with all rights reserved.
The ROV BizStats tool is a very powerful and fast module in Risk Simulator software that is used for running more than 200 business statistics and analytical models on your data. The following provides a few quick getting started steps on running the module and details on each of the elements in the software. Follow these steps for running ROV BizStats (see Figures 8.1–8.4 for screenshots and locations of certain elements), assuming you have already installed either Risk Simulator or ROV BizStats. Start ROV BizStats inside Risk Simulator at Risk Simulator | ROV BizStats or start the standalone ROV BizStats software directly from the desktop icon, and then follow the steps below::
- Step 1. To get started learning the tool, click on the Example button [A] to load the default sample data and model profile or type in your data or Copy/Paste your own data into the data grid [B] from Excel or another software (Figure 8.1). You can add your own notes or variable names in the first Notes row [C].
- Step 2. Select the relevant model[D] to run and enter in the appropriate variables [G]. See area [F] for some example inputs of the selected model as well as short descriptions. Separate variables for the same parameter using semicolons and use a new line (hit Enter to create a new line) for different parameters. (Click on any one of the saved models in Step 4 [J] to see some examples of predefined models and their user inputs.)
- Step 3. Click Run [K] to compute the results [L]. You can view any relevant analytical Statistical Results or Charts from the two tabs [M].
- Step 4. If required, you can provide a model name [H] to Add [I] the model into the profile. Multiple models [J] can be saved in the same single profile. Existing models can be edited or deleted [I] and rearranged in order of appearance [N], and all the changes can be saved into a single profile with the file name extension *.bizstats. The profile can be saved using the menu File | Save or File | Save As [O].
Notes and Reminders
- Saving. Note that the File | Save menu [O] command saves the entire dataset, settings, notes, and created models and computations into a single *.bizstatsfile. As an example, this is similar to saving an Excel *.xlsx file. However, there is also the Add, Edit, and Delete functionality [I] in Step 4 of the user interface to save individual models, input variables, notes, and settings. Think of these saved models [J] as different worksheet tabs in Microsoft Excel. So, you will still need to save the entire *.bizstats file when you are done adding all these models. That is, adding multiple worksheets in Excel works but you still need to save the entire *.xlsx file when done.
- Maximizing User Interface. You can maximize the user interface for larger views of the data grid, results, and charts or use the standard-sized view for easier manipulation of the software. Change between maximized or standardized views by clicking on the relevant Windows form buttons on the top right corner of the software.
- Pasting Data. When copying and pasting your data into the data grid [B] in ROV BizStats, make sure to click on and select the correct single-cell location before pasting (click on and select the location, then CTRL+V or right-click and select Paste Data). Make sure to select a cell in the data grid (this is the top left corner of the data to paste) either starting from the data rows (ROW 1) or from the NOTES row if your copied data has headers.
- Grid Size. The data grid size can be set in the menu, where the grid can accommodate up to 1,000 variable columns with 1 million rows of data per variable. The menu also allows you to change the language settings and decimal settings for your data. Finally, the Data | Auto-Fit Columns [O] allows you to auto-fit the entire data grid at once.
- Load Example. To get started, it is always a good idea to load the example file [A] that comes complete with some data and pre-created models [J]. You can double-click on any of these models to run them and the results are shown in the report area [L], which sometimes can be a chart or model statistics [M or U]. Using this example file, you can now see how the input parameters [G] are entered based on the model description [F], and you can proceed to create your own custom
- Auto-Fit. If a cell has a large value that is not completely displayed, click on and hover your mouse over that cell and you will see a pop-up comment showing the entire value, or simply resize the variable column (drag the column to make it wider, double-click on the column’s edge to auto-fit the column, or right-click on the column header and select auto fit). You can also use the Data | Auto-Fit Columns menu [O] item to auto-fit the entire data grid at once.
- Navigation. Use the up, down, left, and right keys to move around the grid, or use the Home and End keys on the keyboard to move to the far left and far right of a row. You can also use a combination of keys such as Ctrl+Home to jump to the top-left cell, Ctrl+End to the bottom-right cell, Shift+Up/Down to select a specific area, and so forth.
- Adding Notes. You can enter short notes for each variable on the Notes [C] row. Remember to make your notes brief and simple.
- Chart Icons. Try out the various chart icons on the Visualize tab [S] to change the look and feel of the charts (e.g., rotate, shift, zoom, change colors, add a legend, etc.).
- Copy Button. The Copy button [R] is used to copy the Results, Charts, and Statistics tabs in Step 3 after a model is run. If no models are run, then the copy function will only copy a blank page.
- Report Button. The Report button [R] will only run if there are saved models in Step 4 or if there are data in the grid, else the report generated will be empty. You will also need Microsoft Excel to be installed to run the data extraction and results reports, and Microsoft PowerPoint available to run the chart reports. If you have a large number of saved models, it may take a few minutes for the report to finish.
- Load Example Button. When in doubt about how to run a specific model or statistical method, start the Example [A] profile and review how the data is set up in Step 1 or how the input parameters are entered in Step 2. You can use these as getting started guides and templates for your own data and models.
- Languages. The language can be changed in the Language menu [O]. Note that currently there are 12 languages available in the software with more to be added later. However, sometimes certain limited results will still be shown in English.
- View Models List. You can change how the list of models in Step 2 is shown by changing the View drop list [E]. You can list the models alphabetically, by various model categories, and by data input requirements––note that in certain Unicode languages (e.g., Chinese, Japanese, and Korean), there is no alphabetical arrangement and, therefore, the first option will be unavailable.
- Decimals. The software can handle different regional decimal and numerical settings(e.g., one thousand dollars and fifty cents can be written as 1,000.50 or 1.000,50 or 1’000,50 and so forth). The decimal settings can be set in ROV BizStats’ menu Data | Decimal Settings [O]. However, when in doubt, please change the computer’s regional settings to English USA and keep the default North America 1,000.50 in ROV BizStats (this setting is guaranteed to work with ROV BizStats and the default examples).
- Column Headers. Click on the data grid’s column header(s) to select the entire column(s) or variable(s), and once selected, you can right-click on the header to Auto-Fit the column, Cut, Copy, Delete, or Paste You can also click on and select multiple column headers to select multiple variables and right-click and select Visualize to chart the data or click the Visualize button [Q] (Figure 8.2). You can also change the different chart types using the chart drop list [T].
- Data Length. If you need to run models with different data lengths of the same dataset, we recommend simply creating additional data variable columns. This helps simplify tracking and auditing your results. Alternatively, you can use the data row controls between [K] and [M].
- Visualize Data. Click on the variable headers [P] to select one or multiple variables at once, and then right-click to add, delete, copy, paste, or visualize [Q] the variables selected. You can then click on the Visualize tab [S] to see the chart.
- Command. Models can also be entered using a Command console [V/W/X] (Figure 8.3). To see how this works, double-click to run a model[J] and go to the Command console [V]. You can replicate the model or create your own and click Run Command [X] when ready. Each line in the console represents a model and its relevant parameters. Here, you can run all or one selected command, save existing commands as a separate file, or open previously saved commands. Commands allow you to quickly run multiple models at once without the need for clicking around the user interface. Results can also be appended to the bottom, where multiple models are run in sequence, and all the results will be created as a single lengthy report (see the two radio buttons below area M).
- XML Editor. The entire *.bizstats profile (where data and multiple models are created and saved) can be edited directly in XML [Z] by opening the XML Editor from the File menu [Y]. Changes to the profile can be programmatically made here and take effect once the file is saved (Figure 8.4).
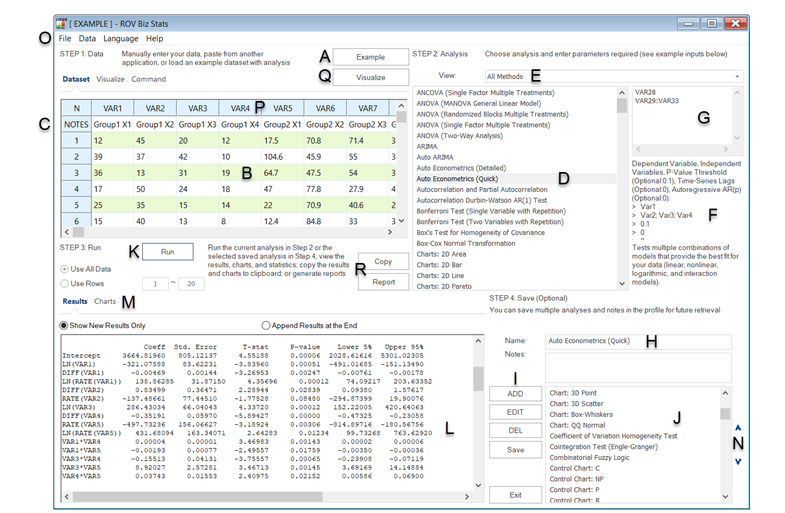
Figure 8.1: ROV BizStats (Statistical Analysis)
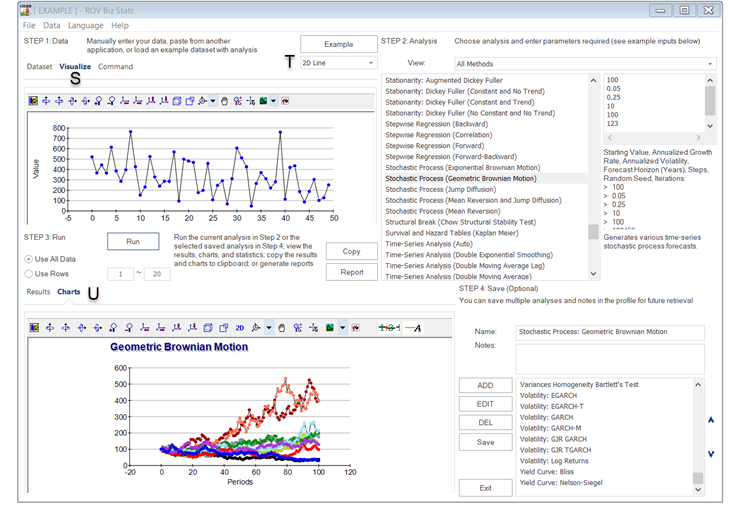
Figure 8.2: Data Visualization and Results Charts
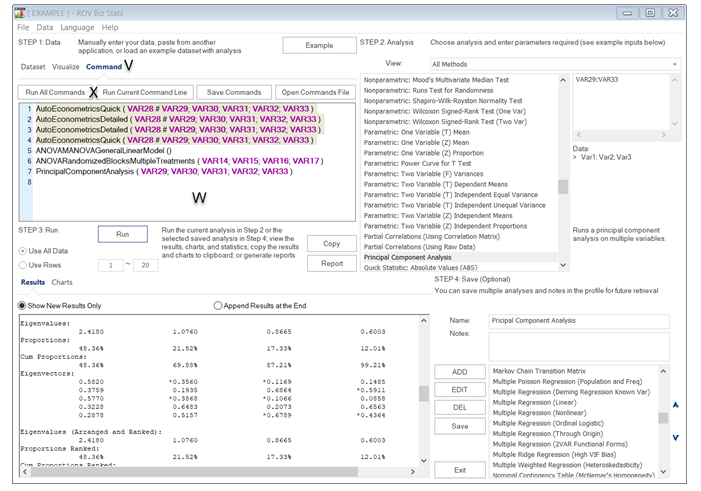
Figure 8.3: Command Console
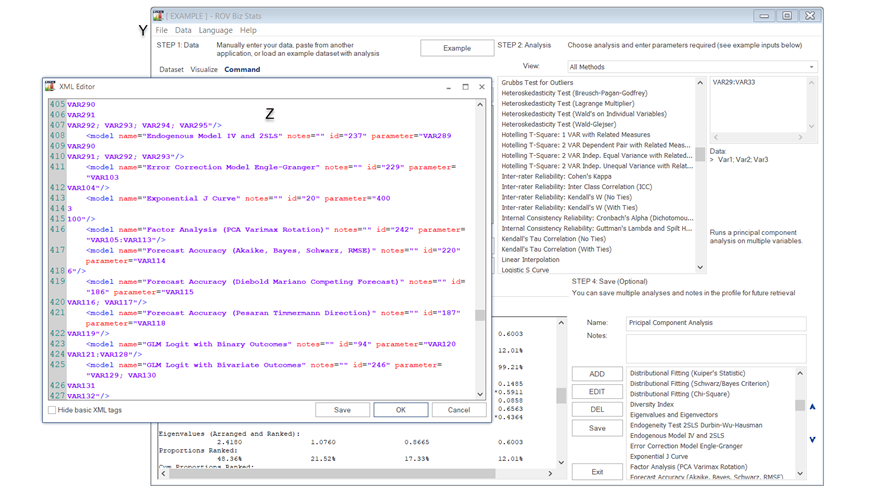
Figure 8.4: XML Editor

